Cancer is a condition where body cells don’t die as they should. These cells keep growing, dividing, but never dying. This accumulation causes these cells to form lumps or tumors. They’re different types of cancers and among them is leukemia. Study made by Chinmay T. Jani, MBBS, Alaaeldin Ahmed, MD, et al., states that, “globally, the annual number of newly diagnosed patients of all leukemias has increased by 46% in the past 3 decades.”
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and the bone marrow. In this case, the body produces too many abnormal white blood cells, which disrupts the balance of healthy blood cells. Abnormal cells don’t work properly, all they do is crowd out the good cells, and make it harder for the body to fight back infections. There are a couple of things you need to know about this condition. This article will be split in two, with this article focusing on the types, symptoms, causes, and stages of leukemia.

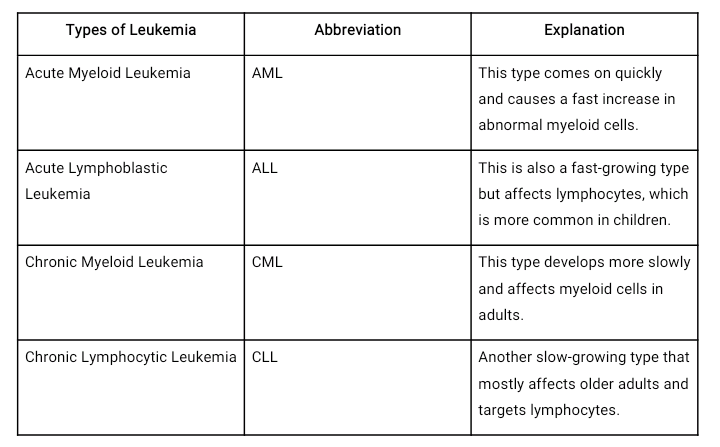
Types of Leukemia
There are four main types of leukemia, namely: AML, ALL, CML, CLL
Common Symptoms of Leukemia
People who are suffering from leukemia will have early symptoms like:
- Tiredness
- Frequent infections
- Bruising or bleeding easily
- Pale skin
- Bone or joint pain
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Weight loss
Causes of Leukemia
The exact cause of leukemia is not always clear. It’s more like a combination of factors that increases the risk of developing the condition over time.
Genetic Changes: Normally, cells in the body have a cycle that they follow: they grow, divide, and eventually die, just like humans. How cells behave is stored in their DNA. But sometimes, a cell’s DNA can get mutated may be as a result of certain environmental causes or just a random occurrence.
Now, when a mutation occurs in the DNA of a developing blood cell, it causes the cell to grow uncontrollably. Instead of maturing into a healthy blood cell, the mutated cell keeps multiplying and doesn’t for when they should have. These abnormal cells build up, and crowd out healthy blood cells, which eventually leads to leukemia.
Exposure to Radiation: Radiation has the ability to damage cells at the DNA level. High doses of radiation, like radiation therapy or a nuclear accident, can penetrate into the body and damage the bone marrow cell’s DNA. This damage mutated the cells and they started to go haywire. Overtime, more and more abnormal cells are produced, causing leukemia.
Similarly, inhaling or having skin contact with certain chemicals like benzene, can damage the DNA of the bone marrow cells. Instead of normal cells multiplying, mutated cells multiply, causing overcrowding and leukemia.
Other Factors: The above mentioned causes are the common causes of leukemia. But there are other causes like smoking, previous cancer treatment, genetic disorder, and family history, that each play their roles in making the risk of leukemia higher.
Conclusion
Nevertheless, across these different causes, the core problem lies in mutations or damage to the DNA of blood-forming cells in the bone marrow. These mutations disrupt the normal cycle of blood cells, causing:
- Uncontrolled growth of immature or abnormal blood cells.
- The abnormal cells crowd out healthy ones, leading to symptoms like infections, bruising, fatigue, and anemia.
- Eventually, a shortage of healthy white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets, which causes many of the health problems seen in leukemia.