One of the many good things about the human body is how it responds to conditions. These responses, which are often in the form of symptoms, give away the fact that something is going on in the body. One of the common body responses is inflammation. That’s also the case for a health condition called Glossitis.
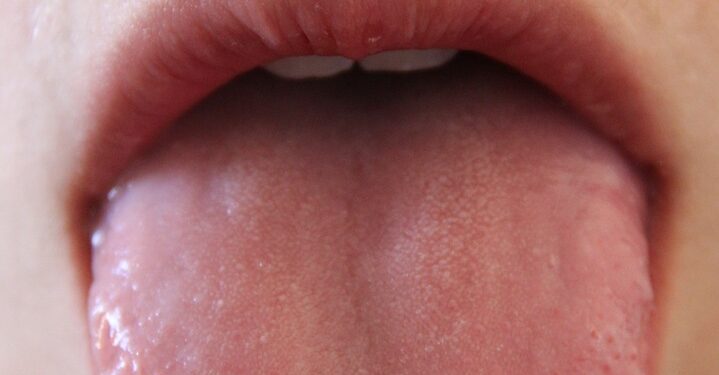
Glossitis is the swelling or inflammation of the tongue as a result of different reasons, causing the tongue to look red and glossy (smooth). This condition can affect people of any age or background. But there are some people who are more likely to develop glossitis. Let’s discuss the process, types, symptoms, and causes of glossitis.
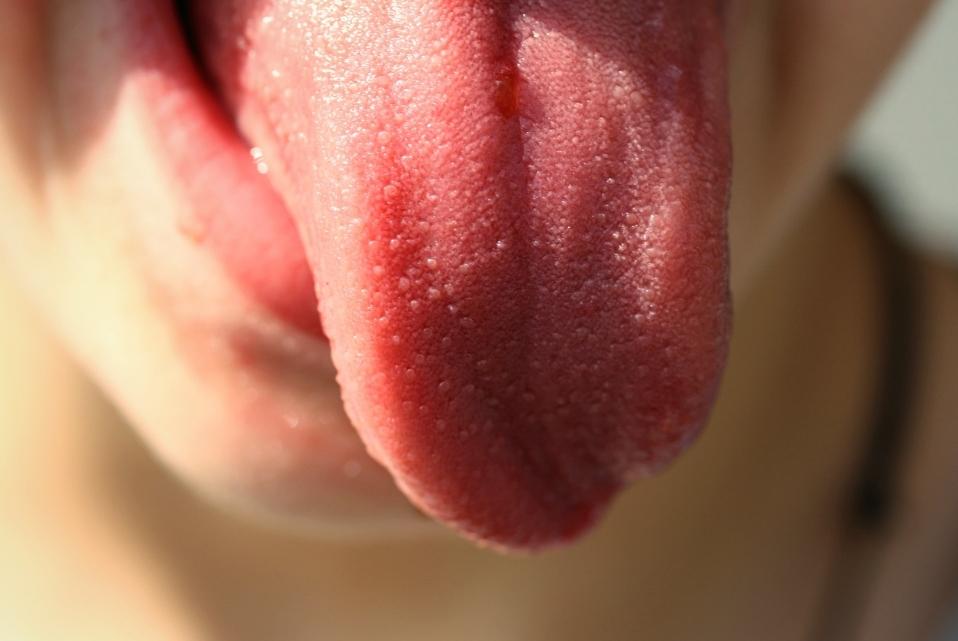
Process of Glossitis
Glossitis often starts with a trigger which affects the cells or the tissue on the tongue. When an infection, a physical injury, allergic reaction, deficiency or dental product disrupts the tongue’s normal state, it can cause irritation or damage to the cells on the tongue’s surface. Once there is damage or irritation, the body responds with inflammation to protect the tongue and begin healing.
Inflammation is the body’s typical way of sending immune cells to the area to help clear out any harmful substances and repair damage. In the case of glossaritis, this inflammation causes the blood vessels in the tongue to widen, which increases blood flow to the area. With increased blood flow, the tongue starts to look redder than usual and may also swell up. This is why an inflamed tongue often appears red and enlarged.
This increased blood flow brings white blood cells to fight off the infection if there is a bacterial, viral, or fungal cause. If the glossitis continues, the tiny bumps on the tongue may start to disappear. This loss of these bumps makes the tongue look smoother and causes the tongue’s texture to change.
Furthermore, these tiny bumps, also known as papillae, also contain taste buds. So when the tongue loses these bumps, it can also affect taste sensations, making the tongue feel different in the mouth. These swollen tissues and exposed nerve endings make the tongue even more sensitive and painful. If the glossitis becomes severe, it can impact the tongue’s regular functions, like chewing and swallowing.
Symptoms of Glossitis
- Pain or soreness in the tongue
- Swelling of the tongue
- Red or inflamed appearance
- Changes in texture (smooth, bumpy, or with grooves)
- Trouble swallowing or speaking
- Reduced sense of taste
Types of Glossitis
Glossitis has a lot to do with appearance. This condition has different types and each of them has its own appearance and causes.
Note: Glossitis is not caused by a single factor, rather it’s caused by different factors like infection, allergies, and deficiencies.
Atrophic Glossitis: This type also known as Hunter’s Glossitis, involves the loss of those tiny bumps on the tongue’s surface, called papillae. When that happens, it gives the tongue a smooth, shiny, and often reddish look.
Atrophic glossitis is often caused by a deficiency, usually in key nutrients like iron, vitamin B12, and folic acid. You’ll mostly notice this type of glossitis in people suffering from diseases like celiac disease.
Median Rhomboid Glossititis: This type of glossititis causes red diamond-shaped patches to appear right in the middle of the tongue, usually towards the back. It is connected to fungal infections like candida, a type of yeast. Candida overgrowth can occur when the immune system is weak, or when the natural balance of microorganisms in the mouth is disrupted. This can happen from prolonged antibiotics use, smoking, or other health conditions like diabetes.
Geographical Tongue: This type is also known as the Benign Migratory Glossititis. It creates map-like patches on the tongue that can change in shape, size, and location over time. These patches are red with white borders, and though they can be really sensitive, they are usually harmless. They usually just come and go. This is usually as a result of triggers like stress, hormonal changes, or irritations to spicy or acidic food.
Allergic Glossititis: As the name implies, this type is caused by allergies. It occurs if the tongue reacts to certain foods, dental products, or medication which causes the tongue to swell and become reddish.
Infectious Glossititis: Infection from bacterial fungi viruses can cause Infectious Glossititis. Bacterial infections happen as a result of poor oral hygiene or dental issues, while viruses like herpes simplex can cause painful sores and inflammation on the tongue. Fungal infections, on the other hand, like thrush, can also cause swelling and pain.
Bottom Line
Glossitis is a way your body shows that something’s wrong by making your tongue inflamed, red, and often sore. It can happen for many reasons; like infections, allergies, vitamin deficiencies, or injuries.