Hydrocephalus can affect both babies and adults. The general concept of hydrocephalus is that the cerebral fluid in the brain whose job is to remove waste from the brain and also protect the (brain + spinal cord) from damage, becomes excess.
However, hydrocephalus is different in infants and in adults. This difference is mainly based on what causes this condition. Infants suffer from hydrocephalus because of some birth defects. On the other hand, adults suffer from hydrocephalus as a result of injury to the brain or as a result of old age. In this article we’ll discuss how hydrocephalus is diagnosed and treated.

How is Hydrocephalus Diagnosed?
Usually, doctors will ask you about how you feel. You’ll describe the symptoms you’ve been experiencing prior to your doctor’s appointment.
After you’ve discussed your symptoms with the doctors, they’ll go ahead to take a better look at what’s happening inside your brain.
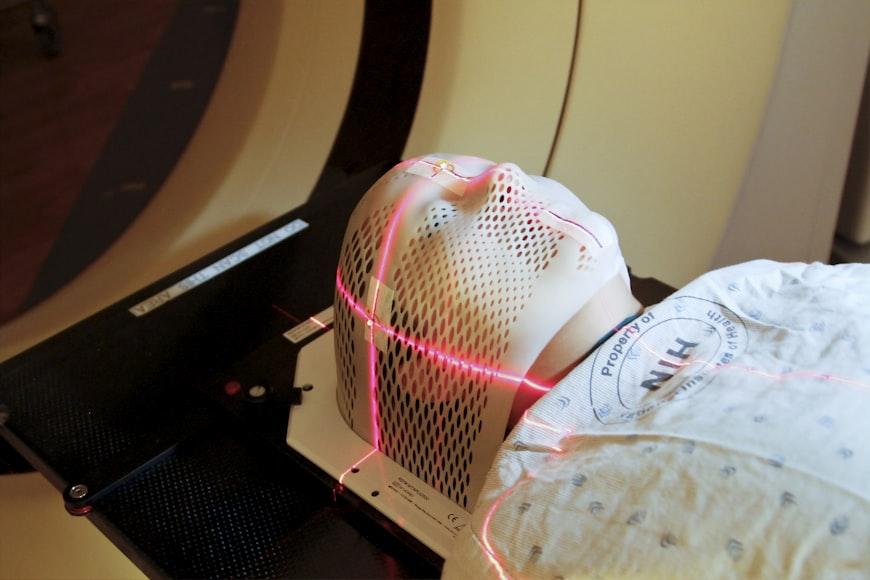
For this, you’ll need to do some imaging tests like a CT scan and MRI. The CT scan allows doctors to see if there is too much cerebrospinal fluid in your brain.
The CT scan images are not really clear which is why an MRI is necessary. This test will create a clearer image of your brain which will help the doctor to spot tumors or cysts in the brain.
Furthermore, there are extra diagnosis procedures that will help the doctors confirm your condition.
- Lumbar puncture: This procedure is also known as the spinal tap, makes use of a small sample of cerebrospinal fluid taken from your lower back to check for infection.
- Intracranial pressure monitoring: In this procedure, doctors use a sensor to keep track of the pressure in your brain.
What Are The Various Treatment Options For Hydrocephalus?
Medication: For some medical conditions, medication is usually a common treatment option and is widely suggested by doctors and pharmacists.
However, medication cannot cure hydrocephalus all by themselves. What medication can do is to manage symptoms like headaches, and infection. They are usually used to support other treatments and are not used as a long-term solution for hydrocephalus.
Shunt surgery: One of the many common treatments is a shunt. This is a small flexible tube that the doctor places in the brain’s ventricles, which are hollow spaces in the brain that contain cerebrospinal fluid. The tube drains the extra cerebrospinal fluid and redirects it to the abdomen, to prevent the fluid from constantly building up in the brain.
Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy: If there’s a blockage in the pathway where the fluid flows, doctors might opt for this treatment option. Doctors use a tiny camera to make a hole in one of the brain’s ventricles, creating a new pathway for cerebrospinal fluid to flow. This new pathway helps to relieve pressure without using a shunt system.
Bottom Line
Hydrocephalus is when there’s too much cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, and it can affect both babies and adults. When treating hydrocephalus, medications are not considered a long-term solution.
They’re only prescribed to help with symptoms, not to cure. However, options like shunt surgery where a tube is used to drain excess fluid away from the brain, and another option called Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy (ETV), are the main treatment options for hydrocephalus.